2. Project Management in GWHAT¶
This document shows how to create, open and manage existing projects in GWHAT. Data are managed in GWHAT by project. This means that all input and output files relative to a particular project are stored in a common folder, hereafter referred to as the project folder. This file management system allows to easily backup or copy the data related to a particular project since all the files are saved at the same location.
Only one project at a time can be opened per instance of GWHAT. The title of the currently opened project is displayed on a button located in the project toolbar as shown in Fig. 2.1. The project named Example is opened by default the first time GWHAT is started. This project includes samples of files to test the different features of GWHAT.
2.1. Creating a new project¶
New projects are created by clicking on the  icon located on the
project toolbar (see Fig. 2.1). This opens a dialog window
(see Fig. 2.2) where information about the project can
be entered such as its title, author, and location coordinates.
icon located on the
project toolbar (see Fig. 2.1). This opens a dialog window
(see Fig. 2.2) where information about the project can
be entered such as its title, author, and location coordinates.
Clicking on the button Save will create a new project folder (named after
the project’s title) and a file with a gwt extension where the information
related to the project are saved.
The directory where the project folder is created can be changed by
clicking the ![]() icon.
The content and format of the project folder
and project file (
icon.
The content and format of the project folder
and project file (*.gwt) are described in more details, respectively, in
Section 2.3 and Section 2.4.
2.2. Opening an existing project¶
Clicking on the button where is displayed the currently opened project title on
the project toolbar (see Fig. 2.1) opens a dialog window where
an existing project file (.gwt) can be selected and opened.
The path to the project folder is stored in a relative format in GWHAT. This means that if the location of the project folder is changed relative the executable of the software (gwhat.exe), GWHAT will need to be redirected to the new location of the project by repeating the procedure described above.
2.3. Project Folders¶
This section describes in details the content of project folders, where are stored all input and output files relative to a particular project. An example of a project folder files organization is presented in Fig. 2.3.
The file with the gwt extension is a binary file where are saved the metadata
related to the project (e.g. project title, author, creation date, etc.). It is also
where are saved all the input and output data related to the plotting and interpretation of
hydrographs, including the estimation of recharge. The format and structure of these
files are described in more details in Section 2.4.
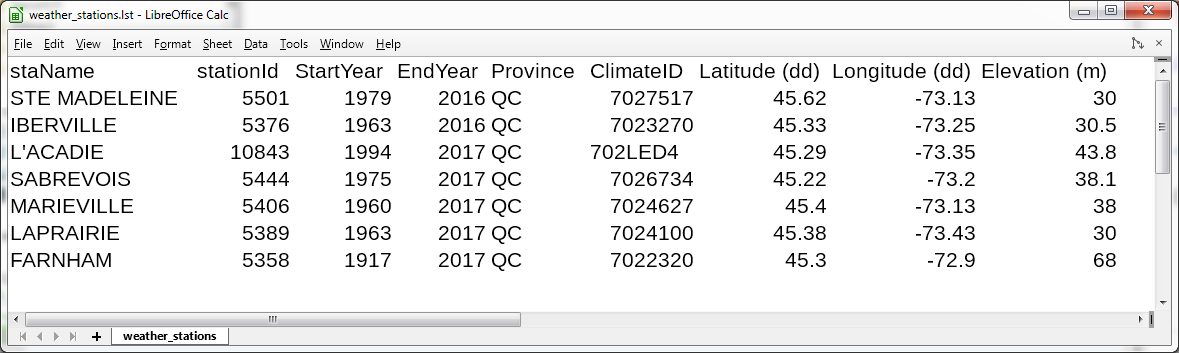
The file with the lst extension is a csv file containing a list of
weather stations from the Canadian Daily Climate Database (CDCD). These files
can be created with the tools presented in Section 4.
An exemple of weather station list is presented in Fig. 2.4.
The file waterlvl_manual_measurements.xls contains the manual
water-level measurements from field visits that are used when plotting the
hydrophraph as explained in Section 6.
The folder Meteo contains all input and output data relative to the
downloading, formatting, and the creation of gapless daily weather records. It
contains three sub-folders named respectively Raw, Input,
and Output.
The folder Raw is where are saved the daily weather data files once they
have been downloaded from the CDCD as described in Section 4.1.
All the files downloaded for a same station are saved within a common folder,
named after the name of the station and its climate ID. For example,
in Fig. 2.3, the data file
eng-daily-01011980-12311980.csv, which contains weather data from the station Marieville
for the year 1980, is saved in a folder named MARIEVILLE (7024627), where the number in
parentheses is the climate ID of the station.
The folder Input is where are saved by default the formatted weather
data files generated from the raw data files. The csv files are named by
default after the name of the station, its climate ID, and the first and last year of the data record.
This folder is also the default location used by the tool to fill the gaps in
daily weather data records to look for input weather data files as described in
Section 5.1.
The folder Output is where the gapless weather time-series are saved in
csv files with the extension .out. The files with the extension .log
are csv files that contain detailed information about the missing
daily weather values that were estimated to fill the gaps in the weather datasets.
The files with the extension .err contains a time-series of estimated weather
values that were produced with a crossvalidation re-sampling technique.
These estimated values can be used to evaluate the accuracy of the method.
The file weather_datasets_summary.log is a csv file that contains a summary
of all the weather data files that are saved in the Input folder.
The folder Water Levels is the preferred location where the water level
datasets related to a same project should be stored. These files can be either
in a csv, xls or xlsx file format.